The dhoni is one of the iconic images of this iconic destination. In particular, its scimitar-like flared bow sprit give it a tell-tale aesthetic signature which lends itself to all sorts of artistic application. The latest example I have found is Rahaa’s Dhirun Bar. I especially appreciate the rooftop deck which simulates the flat-top perch on covered dhonis that we enjoy sunbathing on with an extra bit of perspective across the blue tapestry of the Laccadive vistas. I also appreciate when resorts put a bit of extra care into designing their bar areas since chilling with a tropical cocktail is such an essential and memorable part of any Maldives stay (and as such, I have added a “Bar” tag).
Best of the Maldives: Biggest Pool Breakfast – Brennia Kottefaru
“We’re gunna need a bigger boat!” – Martin Brody
No, not for thing eating you in the water…for you eating things in the water. And Brennia Kottefaru has delivered with the biggest boatload of breakfast we have seen. (thanks Ibrahim)
Best of the Maldives Online: Shipwreck Guide – “Shipwrecks of the Maldives”
The Maldives’ shallow atolls might make for spectacular lagoons and particularly accessible snorkelling, but they were nightmarish obstacle courses for the seafaring trading ships of plying the East-West trade centuries ago. While the wooden vessels have long since rotted away, more modern ones have hit these lurking reefs plenty of times in recent years. In fact, enough to fill a book, “Shipwrecks of the Maldives” by Peter Collings. Not only is it full of dozens of wrecks that I wasn’t aware of (despite having nearly 2000 site in the Dive Site database), but most of them are meticulously researched about their history and background.
I was fortunate to catch up with author Peter Collings who provided a bit more background on his work for Maldives Complete:
- What got you into wreck diving? – During the early expeditions in southern Egypt (1995), I brought together divers from all agencies-with a common goal to explore new locations looking for shipwrecks and unearthing their stories. Endorsed by the Red Sea Association, it soon became an international club which included divers from all walks of life with very useful skill sets, and non divers within the archival services of the world. It became the leading body of wreck research, and still is, in Egypt. To date the team have located, identified and surveyed 34 of the wrecks dived in Egyptian waters.
- When did you first visit the Maldives? – 1995.
- How long did the book take to write? – Three weeks.
- Are there any aspects of wrecks in the Maldives that are a bit different to wrecks in other parts of the world? – Most wrecks there are deliberately sunk for tourists.
The book is available as an ebook PDF here.
Best of the Maldives: Catamaran Transfer – SAii Lagoon / Hard Rock
After 20+ years of travelling to the Maldives, I’m regularly surprised to find somewhat simple things that I’ve never seen before. The latest was our transfer to SAii Lagoon and Hard Rock on a catamaran speed boat. On one hand, cats are much more stable than mono-hulls, so you would think that they would be a prominent choice to provide the smoothest final leg to your Male atoll resort. But, they are more expensive so I can understand resorts choosing the lower cost vessel. One of their biggest advantages is capacity and for smaller resorts, you often don’t get more than a few folks transferring per arrival so that space is probably not worth it. But SAii Lagoon and Hard Rock (plus day visitors at The Crossroads) is a bigger complex so they can justify the expense carrying the larger boatloads.
Best of the Maldives: Shortest Private Jet Transfer – NIYAMA
The major point of a private jet is to avoid stopovers and transfers and just get directly from point A to point B. With so many of the super-luxury resorts a plane ride away from the main airport in Male, the most affluent look to fly their private jet straight to their island. No resorts have their own private jet runaway, but NIYAMA is a mere 7 minute boat transfer from the newly opened Dhaalu Airport.
Dhaalu Airport can now handle and process long range jets up to 111 feet in length, with ninety-six hours’ notification required to arrange a private international landing and departure, including immigration, customs and legislated health checks and requirements for arriving passengers.
I wouldn’t have included NIYAMA in the list of “super-luxury” properties that most of the private-jet-set would frequenting, but maybe this convenience will boost their appeal.
No, The Maldives Doesn’t Suck At All
I don’t know if this Top Tens writer had a few too many Guinness’s (Happy St. Patrick’s Day today) when writing this piece or whether they were just trying to be as provocatively counterintuitive as possible for click-bait. But nonetheless, I am open-minded and thought I would check out their “10 Beautiful Places in the World That Actually Kinda Suck”. The video piece not only featured the “Maldives” at #4, but actually highlighted it as their splash image to the video.
I wondered if they were just going to harp on some esoteric, quirky aspect of the destination with a semi-justified albeit tongue-in-cheek winge. But as it turns out, their piece appears to be as completely serious as it is completely misinformed. It’s like they didn’t even bother to do any proper to do any proper research and chose instead to parrot some schoolyard gossip that they heard about this popular cool kid who they envied.
I thought about correcting their errors here, but instead I chose to try my hand at my first Maldives Complete “reaction video”. As it happens, I’ve been quietly been posting videos to my “Maldives Complete” YouTube channel primarily as a way to conveniently host videos for sharing here. But as “Subscribe” is the new “RSS”, please hit the “Like” and “Subscribe” button if you want me to do more videos.
Best of the Maldives: All You Can Stay – Anantara Veli
Not only are the Maldives leading the way with their own vaccinations, but they are also investigating extending that effort to guests themselves:
- “The Maldives is contemplating the introduction of vaccine tourism across its collection of over 200 resort islands, as tourist arrivals begin to grow in the post-pandemic era… He added that the currently available Covid-19 vaccines require two doses of the vaccine to be received within a 10-week period – meaning, there is a significant window of time between the inoculation of the two doses in which tourists could stay in the Maldives. According to Mausoom, the Maldives is likely to become one of the first countries to have vaccinated its entire population, making it one of the safest destinations to visit.”
The best part is the name – “vaxication”.
As the pandemic has not just made remote working more acceptable, but in many cases, downright preferable, some executives are thinking that if you are going to be stuck somewhere, why not make it paradise? Whether you want to have an extended stay (and I mean exteeeeeeended) either to wait for your vaccine second dose, or just to luxuriate in the best workplace on the planet, then Anantara Veli is offering a rate to cover the entire YEAR:
- “Imagine escaping to your very own over-water home retreat in the Maldives at the drop of a hat. Now with Anantara Veli Maldives Resort’s ‘Unlimited Stays in Paradise’ package, you can book unlimited nights at the resort for a one-time fee and make this island paradise your bolthole for the duration of 2021.”
“All You can Sleep” Buffet!
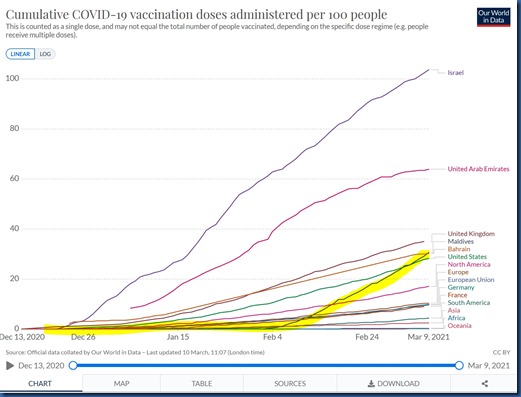
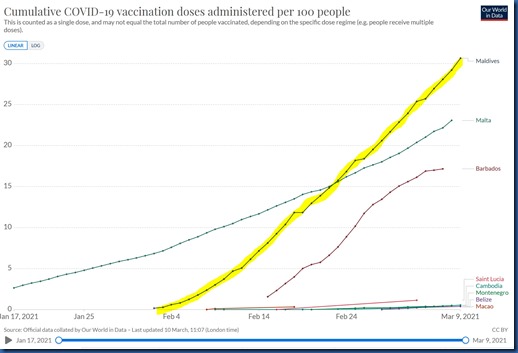
Maldives Vaccination Leadership
The Maldives is en route to another world leading mark – the country getting the highest proportion of its population vaccinated the fastest. Already, they have one of the highest proportion of their country vaccinated. For countries over 100,000 in population, the Maldives is only surpassed by Israel, OAE and the UK. And their current rate of penetration surpasses everyone.
As I noted in my December visit, with so much of their economy dependent on tourism (in fact, the highest proportion of GDP in the world), the pandemic’s effect on travel means a double whammy to their country from this disease. From the outset, they have had strong incentive to tackle COVID-19 and to make extra investments in ensuring the safety of their destination. And that includes aggressive vaccination of the population especially in recent weeks. Of the Top 20 counties with the highest dependency on tourism, the Maldives was the runaway leader in proportion of population vaccinated (of countries over 100k population, see chart below).
Those investments appear to be paying off. Maldives visitor numbers have rebounded strongly. In fact, the Maldives appears to be turning adversity to advantage as many people around the world are extra keen on the Maldives’ distinctive isolation to protect themselves during the pandemic. And as lock-downs have transformed the degree to which people can and do work remotely, people have all the more freedom to escape to the Maldives and work from there. If you are forced to hunker down and avoid contact with people, what better place to do it than a villa in paradise?
Best of the Maldives: Thali – Faarufushi
For variety of local flavours served up on a flat cake, Faarufushi offers a range of Thali taste treat.
- North Indian
- Shakhahari
- Maldivian
Thali is used to refer to an Indian-style meal made up of a selection of various dishes which are served on a platter. Sort of a tapas of the subcontinent. Executive Sous Chef Bir Kumar Yadav (photo below) is always introducing new options for an ever changing palete palatte.
Best of the Maldives: Pancakes – Joali
My biggest laugh this week was a gem of a line in the bio-pic flick “Judy” (about Judy Garland) which during a visit to London says, “You ever tried a crumpet?…Mm?…It’s like a pancake that’s had the living sh*t kicked out of it” (I couldn’t have put it better…if you visit London, don’t order the “crumpets” no matter how daintily British they sound). As an American by upbringing, we take our pancakes extremely seriously. I have yet to find the level of griddle cake quality in the UK that is standard fare in the USA. And, the same is true for most of the chewy circles serves at some of the resort buffets. Until we came to Joali. They have a special a la carte pancake menu including some savoury versions that are simply delicious:
- Spiced Jaggery, fresh coconut
- Cinnamon, prunes, honey
- Banana, yoghurt, strawberry, mint
- Chocolate, walnut
- Exotic tropical fruit
- Mixed berry, sweet mascarpone
- Savory tuna tapenade, olives, remoulade
- Sweet corn, cherry tomato salsa, crispy bacon
I had the spiced Jaggery (an unrefined sugar in Asia) and it was truly delicious (see photo above). Or as Lori and I would say for recipes we like, “a do-again”. A more-ish classic dish with a distinctly Maldivian twist.